Table of Contents
Toggle1. What is August 2025? Spam Update and why is it important?
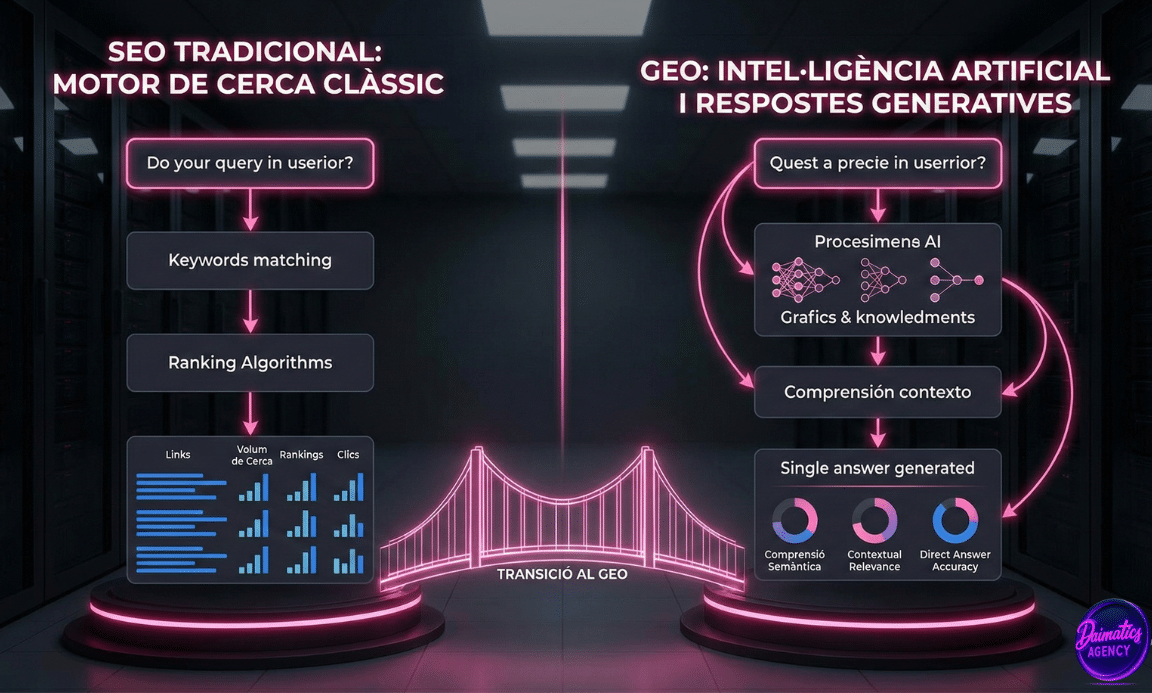
Google has moved the pieces again with a new algorithm update focused on fighting spamThe so-called August 2025 Spam Update began rolling out in late August and was completed on September 22. This update expands the focus on deceptive techniques that harm the search experience, spotlighting practices such as link spam, mass-generated content, abuse of expired domains, and partnerships that leverage a domain's reputation to position low-quality content.
Main objectives of the update
Google's stated goal is clear: "to ensure useful, reliable, and user-oriented results." This update seeks to eliminate content that attempts to manipulate rankings through tricks, and reward websites that generate real value. This includes:
- Reduce automated content that does not provide human value.
- Prevent high-authority sites from hosting third-party content for unethical positioning.
- Penalize the use of expired domains used to gain rankings without thematic coherence.
Differences from other updates such as core updates
Unlike the core updates, which affect the entire Google content rating system, this update is specific to techniques of spamThis means that it does not necessarily affect well-optimized content, but rather those sites that violate the policies of spam officials.
2. Update deployment timeline
Key dates: Start and end
TheAugust 2025 Spam Update began to unfold August 22, 2025 and was completed a month later, the September 22During this period, many sites experienced significant changes in organic traffic, especially in sectors such as media, affiliate blogs, and eCommerce with automated or mass content.
Types of websites affected
The most affected places were those that:
- They published hundreds or thousands of similar pages with little added value.
- They used purchased domains that previously had authority to host unrelated content.
- They allowed third parties to publish content without editorial control (abuse of domain reputation).
3. Most notable changes in the update
Penalty for mass-generated content
One of the red lines of this update is the publication of scaled contentGoogle now penalizes automatically generated pages with repetitive patterns more severely, especially if they do not provide new, useful or reliable information for the user.
Abuse of expired domains
Using expired domains to try to maintain previously obtained rankings is now a highly risky practice. If there is no thematic coherence, transparency i added value, Google may ignore legacy signals or even apply penalties.
Site reputation abuse and uneditorial practices
Sites that allow external collaborations or posts must ensure that they meet the site's editorial standards. If third parties are allowed to post promotional, affiliate, or low-quality content, this is considered abuse of domain reputation, and can have serious consequences on the overall visibility of the site.
4. How to know if your website has been affected
Signals in organic traffic and impressions
One of the first signs is a sudden or sustained drop in organic traffic. However, you should also watch for:
- Reduction of impressions or clicks in Search Console.
- Loss of key positions in branded or high value words.
- Deindexing specific pages or entire sections.
Use of Google Search Console for diagnosis
The best tool to identify impacts is Google Search Console. Review performance reports, especially by sections or content types. You can also:
- Filter by device, country, and URL to detect patterns.
- Check for indexing or coverage errors.
- Review inquiries with significant loss of visibility since the end of August.
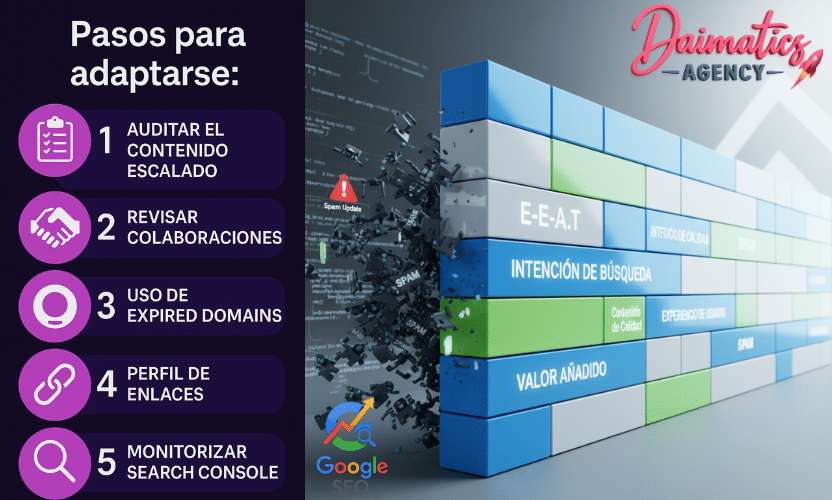
5. Checklist seo post-update: 7 critical steps
To adapt to the update and improve the situation, we recommend that you follow this quick action checklist:
1. Content audit
Review all recently published content. Remove or improve pages that:
- Whether repetitive, automated or of little value.
- They have no visits or incoming links.
- They do not respond to a clear search intent.
2. Management of suspicious links
Review your inbound link profile. Remove or disallow those that:
- They come from low-quality link networks or directories.
- Whether they are clearly artificial or exchanges.
- They provide no real context or authority.
3. UGC and comments
User-generated content (UGC) can be a weak point. Make sure to:
- Apply antispam filters and manual moderation.
- Use attributes
rel="ugc"orrel="nofollow"on links from unknown users. - Temporarily unindex content with low reputation until reviewed.
4. Control of external collaborations
If you allow third-party articles, please ensure:
- Editorial review before publishing.
- Label
nofollowfor commercial links. - Make sure the content is relevant to your audience.
6. Specific recommendations for eCommerce, media and blogs
eCommerce: focus on original descriptions and transparency
E-commerce sites should prioritize their own product descriptions, avoid duplicate suppliers, and add value with reviews, videos, or comparisons. Transparency in terms of sales, returns, and contact information is essential to build trust and avoid penalties.
Media and editorial content: review, authorship and added value
News portals and blogs must reinforce their credibility by showing clear authorship of articles, information about editors, update dates and sources. Google values content with a robust and traceable editorial structure much more.
7. Best practices that Google wants to see on your site
Content for people, not algorithms
The "people-first content" paradigm involves writing with the reader in mind, not rankings. This means:
- Resolve specific doubts clearly.
- Avoid keyword stuffing or artificial phrases.
- Prioritize narrative quality and logical structure.
Transparency and reliability: sources, review and updating
Google rewards websites that indicate:
- Who wrote the article and what is their experience?
- When it was published and whether it has been reviewed recently.
- What sources were used to write the content.
8. Common mistakes that can lead to penalties
Cloaking, keyword stuffing and link networks
Even today, many websites continue to apply penalized practices such as displaying different content to users and search engines (cloaking), repeating keywords in an unnatural way, or participating in link networks. These techniques have a high risk of being penalized.
Repurposing expired domains without adding value
Buying a domain with historical authority and using it for an unrelated project, with no added value, is considered spamTo do it correctly:
- Ensures thematic relevance.
- Explain the use of the domain to users (transparency).
- Avoid keeping old content just to maintain ranking.
9. What does Google say about recovering a penalized site?
The time it takes for the system to reevaluate
Google says that recovery is not immediate. Its systems need time to re-evaluate a site's signals and determine whether it is now in compliance with policies. This re-evaluation can take time. weeks or months, depending on the size and crawl frequency of the site.
Best practices for effective recovery
To recover your ranking after a negative impact:
- Document all changes made.
- Don't make changes every day; wait and measure.
- Avoid continuing with risky practices.
- Use Search Console to detect improvements by section.
10. August 2025 Spam Update vs previous updates
Comparison with updates from 2024 and early 2025
The updates of spam of 2024 were already pointing to the use of generative AI and scaled content, but in August 2025 Spam Update takes it to a higher level. Now also penalizes tactics of website reputation abuse and expired domains, something that didn't have as much weight before.
Repeated patterns and new criteria
Some patterns remain constant (like the link spam), but Google is adding new criteria such as the origin of the content, the author's expertise, and the relationship between the domain and the topic of the content. These aspects are expected to carry even more weight in future updates.
11. The future of seo according to recent Google changes
From quantity to quality: a new era of content
The signs are clear: more is not better. Google wants websites with fewer pages, but more useful, more complete and more reliable ones. We need to leave behind the “one article for each keyword” model and focus on complete, user-oriented guides.
The impact of AI and automatically generated content
The use of artificial intelligence tools to generate content is acceptable only if:
- The article is reviewed and improved by humans.
- It provides original value and is not a copy of other sources.
- It is not used to create mass or misleading content.
12. Structured data and rich results: how to adapt
Removal of obsolete types
Google has started removing support for certain types of structured data. It is essential to review your schema.org and make sure you only use currently supported elements, such as:
- Article
- Product
- FAQ Page
- HowTo
- Review
Optimal implementation according to official guidelines
Follow the instructions of Google Search Central to ensure that your implementation is valid. Use the official validator and avoid “forcing” structured data that is not reflected in the actual content.
13. Real cases: penalized sites and recovery strategies
Examples of sites that have lost visibility
Some news portals, content aggregators, and eCommerce sites with massive product sections have seen traffic drops from 30% to 70%. In many cases, these were auto-generated pages or pages with duplicate content.
Actions that have led to recovery
- Remove duplicate or low-quality content.
- Improve the web architecture to make it clearer and more hierarchical.
- Reduce the number of commercial or affiliate outbound links.
- Add authorship information and review sources in each article.
14. Useful resources and official documentation
- Policies of spam from Google
- Update Guide spam
- Create useful and reliable content
- Preventing abuse of UGC and spam of users
- Google core update guide
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What can I do if my website has been penalized?
Review your content and remove anything that is superficial, repetitive, or doesn't add value. Also review your link profile and third-party content.
How long does it take for a site to recover?
It depends on the size of the site and the nature of the problem. In general, it can take from 4 weeks to 3 months.
What are the most common errors that this update penalizes?
Mass-generated content, abuse of expired domains, unnatural linking practices, and hosting low-quality external content.
AI content is considered spam?
Not necessarily. If it is well written, reviewed and provides new value, it is valid. But if it is automatically generated and published en masse, it can be penalized.
How can I control user-generated content (UGC)?
Moderate comments, apply antispam filters, use attributes like rel="ugc" and consider adding noindex temporary for new users.
What does "site reputation abuse" mean?
This is when a website hosts third-party content that benefits from the domain authority, but doesn't meet the same quality standards.
16. Close the circle: think strategically and long-term
Your success on Google will never depend on a single update, but on your ability to generate real, sustained and user-oriented valueIf your site has been affected, don't take it as a punishment, but as an opportunity to refocus your strategy. Adopt a mindset of constant evolution, follow official guidelines, and build a digital asset that lasts.